Transpiration
Exercise 2
Solution A.1.
(a) Open stomata, dry atmosphere and moist soil
Solution A.2.
(a) increase
Solution A.3.
(b) temperature is high
Solution A.4.
(c) sunken stomata
Solution A.5.
(d) hydathodes
Solution A.6.
(d) transpiration
Solution A.7.
(d) hot, dry and windy
Solution A.8.
(b) Lenticels
Solution A.9.
(b) evaporation of water from the aerial surfaces of a plant
Solution B.1.
(a) Lenticels
(b) Guttation
(c) Potometer
(d) Nerium
(e) Ganong’s photometer
(f) Stomata and cuticle
(g) Hydathodes
(h) Guttation
Solution B.2.
(a) vapour, aerial
(b) stomata, transpiration
(c) suction, water (heat)
Solution C.1.
(a) guttation
(b) protection and reduced transpiration
(c) transpiration
(d) reduced transpiration
Solution C.2.
(i) False
(ii) True
(iii) True
(iv) False
(v) Most transpiration occurs at mid-day.
(vi) Potometer is an instrument used for measuring the rate of transpiration in green plants.
Solution C.3.
(a) Transpiration increases with the velocity of wind. If the wind blows
faster, the water vapours released during transpiration are removed
faster and the area surrounding the transpiring leaf does not get
saturated with water vapour.
(b) When the rate of transpiration far exceeds the rate of absorption of water by roots, the cells lose their turgidity. Hence, excessive transpiration results in wilting of the leaves.
(c) Plants absorb water continuously through their roots, which is then conducted upwards to all the aerial parts of the plant, including the leaves. Only a small quantity of this water i.e. about 0.02% is used for the photosynthesis and other activities. The rest of the water is transpired as water vapour. Hence water transpired is the water absorbed.
(d) There are more stomatal openings on the lower surface of a dorsiventral leaf. More the number of stomata, higher is the rate of transpiration. Hence more transpiration occurs from the lower surface.
(e) Cork and Bark of trees are tissues of old woody stems. Bark is thick with outermost layer made of dead cells and the cork is hydrophobic in nature. These properties make them water-proof and hence they prevent transpiration.
(f) In both perspiration and transpiration, water is lost by evapouration from the body of the organism as water vapour. This evaporation reduces the temperature of the body surface and brings about cooling in the body of the organism.
(g) On a bright sunny day, the rate of transpiration is much higher than any other days. The leaves of certain plants roll up on a bright sunny day to reduce the exposed surface and thus reduce the rate of transpiration.
Solution C.4.
(a) False
Reason: Potometer is used to measure the rate of transpiration in a
plant. Demonstration of transpiration occurring from the lower surface
of a leaf is done by analyzing the changes in colour of pieces of dry
cobalt chloride paper attached (and held in place) to the two surfaces
of a leaf.
(b) True
Reason: Transpiration carried out by the large number of trees in a
forest. This increases the moisture in the atmosphere and brings rain.
(c) False
Reason: Hydathodes are special pores present on the ends of leaf veins
through which guttation occurs and water droplets are given out. Their
openings cannot be regulated. Stomata on the other hand are minute
openings in the epidermal layer of leaves through which exchange of
gases as well as transpiration occurs. Water is given out as water
vapour. Stomatal opening is regulated by guard cells.
(d) False
Reason: Transpiration is reduced during high atmospheric humidity. High
humidity in the air reduces the rate of outward diffusion of the
internal water vapour across stomata, thereby reducing the rate of
transpiration.
(e) True
Reason: Desert plants need to reduce transpiration as much as possible
so as to survive in the hot and dry environment. Hence some of them have
sunken stomata as an adaptation to curtail transpiration.
(f) True
Reason: During the day, the stomata are open to facilitate the inward
diffusion of carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. During mid-day, the
outside temperature is higher, due to which there is more evaporation of
water from the leaves. Therefore more transpiration occurs during
mid-day.
Solution C.5.
| Guttation | Bleeding |
| It is the removal of excess of water from the plants because of excess water buildup in the plant. | It is the removal of water from the plant because of injury. |
| Water escapes from specialisedstructures called hydathodes. | Water escapes in the form of sap from the injured part of the plant. |
Solution D.1.
Wilting refers to the loss of cellular turgidity in plants which results
in the drooping of leaves or plant as a whole because of lack of water.
During noon the rate of transpiration exceeds the rate of absorption of
water by roots. Due to the excessive transpiration, the cells of leaves
lose their turgidity and wilt.
Solution D.2.
The lower surface of leaf is sheltered from direct sunlight. If more
stomata are on the upper surface of a leaf, then excessive transpiration
would occur, resulting in quick wilting of the plant. Hence most plants
have more numerous stomata on the lower surface of a leaf to control
the rate of transpiration.
Solution D.3.
Take the small potted rose plant and cover it with a transparent
polythene bag. Tie its mouth around the base of the stem. Leave the
plant in sunlight for an hour or two.

Drops of water will soon appear on the inner side of the bag due to the
saturation of water vapour given out by the leaves. A similar empty
polythene bag with its mouth tied and kept in sunlight will show no
drops of water. This is the control to show that plants transpire water
in the form of water. If tested with dry cobalt chloride paper, the
drops will be confirmed as water only.
Solution D.4.
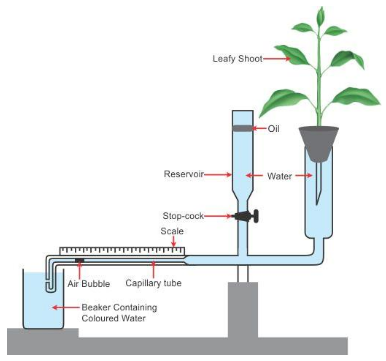
Potometer is a device that measures the rate of water intake by a plant.
This water intake is almost equal to the water lost through
transpiration. Potometers do not measure the water lost due to
transpiration but measure the water uptake by the shoot.
Solution D.5.
- Transpiration occurring through lenticels i.e. minute openings on the surface of old stems is called lenticular transpiration.
- Stomatal transpiration is controlled by the plant by altering the size of the stoma, where as this does not happen in case of lenticular transpiration. This is because the lenticels never close, but remain open all the time.
- The amount of stomatal transpiration is much more than the amount of lenticular transpiration.
Solution D.6.
The factors that accelerate the rate of transpiration are:
- High intensity of sunlight
- High temperature
- Higher wind velocity
- Decrease in atmospheric pressure
(Any three)
Solution D.7.
Forests have large number of plants especially trees. Each plant loses
water in the form of water vapour everyday into the atmosphere through
transpiration. A large apple tree loses as much as 30 litres of water
per day. So huge amount of water is escaped into the atmosphere by
forests. This increases the moisture in the atmosphere and brings more
frequent rains.
Solution D.8.
The advantages of transpiration to the plants are:
- Transpiration brings about a cooling effect to the plant body since evaporation of water reduces the temperature of leaf surface.
- Transpiration helps in the ascent of sap by producing a suction force acting from the top of the plant.
- Transpiration helps in distributing water and mineral salts throughout the plant body.
- Transpiration helps in eliminating excess water.
Solution D.9.
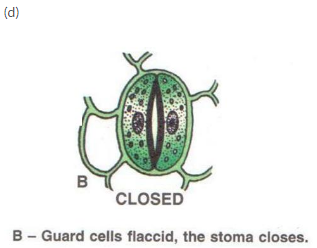
- If the water content of the leaves decreases due any reason, the guard cells turn flaccid, thereby closing the stomatal opening and transpiration stops.
- Some plants have sunken stomata whereas others have reduced number of stomata to reduce transpiration.
- In some plants, leaves may be dropped or may be absent or changed into spines as an adaptation to reduce transpiration.
- The leaves may be covered by thick cuticle such as in Banyan tree, so as to reduce transpiration.
Solution D.10.
No, they are not dew drops.
This is water given out by the plant body through guttation. Since the banana plant is growing in humid environment, transpiration is hampered. But the roots continue to absorb water from the soil. This builds up a huge hydrostatic pressure within the plant and forces out the excess water from the hydathodes, which are pores present at the tips of veins in the leaf. This is observed especially during the mornings.
Solution D.11.
(a) Intensity of light – During the day, the stomata are open to
facilitate the inward diffusion of carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. At
night they are closed. Hence more transpiration occurs during the day.
During cloudy days, the stomata are partially closed and the
transpiration is reduced.
(b) Humidity of the atmosphere – When the air is humid; it can receive
very less water vapour. Thus, high humidity in the air reduces the rate
of outward diffusion of the internal water vapour across stomata,
thereby reducing the rate of transpiration.
Solution E.1.
(i) The leaf D would become most limp. This is because water would be lost through transpiration from upper as well as the lower surface of leaf D since it is uncoated.
(ii) The least limping would be shown by leaf C since its upper and lower surfaces have been coated with vaseline. So no water is lost from the leaf through transpiration since the stomatal openings get blocked by vaseline.
Solution E.2.
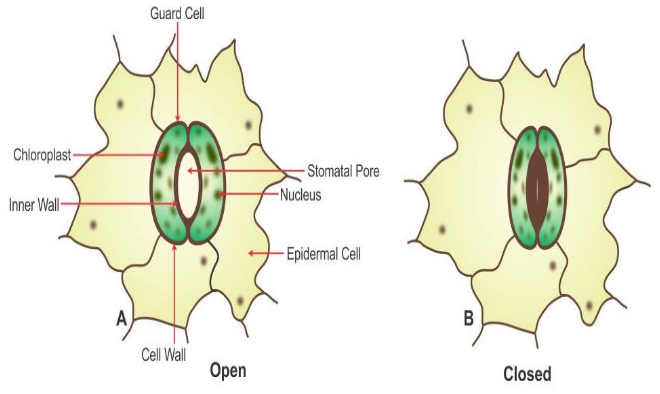
(a)
Guard Cell
Inner wall of the Guard Cell
Stoma/Stomatal Aperture
(b) Open state
(c) The structure of stoma remains same in monocots as well as in
dicots. Hence, the stoma from the diagram can be of a monocot leaf or of
a dicot leaf.
Solution E.3.
(a) Transpiration
(b) Oil is put on the surface of water to prevent loss of water by evaporation.
(c) Yes, the transpiration rate will increase. Transpiration would occur faster. The observable changes will occur in less time.
(d) The spring balance progressively measures the change in weight of
the set-up. This because as the plant transpires, it creates the suction
force in plant which allows roots to absorb more water from the test
tube. Hence, the water in the test will get reduced. Thus, the weight of
the entire set will decrease.
Comments
Post a Comment